How To Perform Cloning
First
we'll cover a bird's eye view of the basic steps to
perform a clone of a cell:
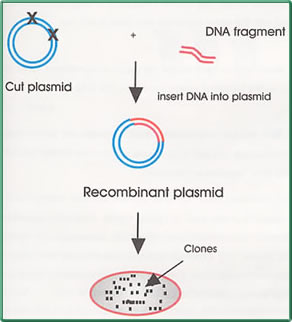 Cut a gene at specific regions or anywhere with
specialised enzymes know as restriction enzymes. Cut a gene at specific regions or anywhere with
specialised enzymes know as restriction enzymes.
- Cut the vector, carrier (frequently a large harmless
virus), usually with the same enzymes you used to
cut the gene.
- Insert or glue the DNA into the cut vector at the
locations the cuts were made
- The current state of the process is called "recombinant
DNA". Place it into bacteria or yeast.
- The yeast or bacteria will grow very fast and in
big quantities. Clones will be made from it. They
may either contain the vector alone, the vector with
the specific foreign DNA, or monster DNA made up of
a very strange combination of the vector and me.
- Finally, inject the recombinant DNA into a cell.
Now, the cell has the DNA piece for the eye colour
gene.
To explore the individual steps in detail, view Part
1 of 4 series of steps.
|

