Protein Translation
If you were going to translate your notes from English
to Russian, you would need a translation dictionary.
Something that tells you how a word in English is written
in Russian, and the translation of protein is no different.
When you move from the language of nucleotides to the
language of amino acids, you still need a "dictionary",
something that tells you which nucleotides correspond
to which amino acids.
More specifically, you need something
to tell you which sequence of three nucleotides corresponds to which one amino acid. A sequence
of three nucleotides is called a codon, and the
order of codons on mRNA specifies the order of amino
acids in a protein.
The dictionary for protein translation
is called the Genetic Code.
Because there are four possible nucleotide bases, and
codons are groups of three bases, there are 64 (4 x 4 x 4) possible codons. Because there are only
20 different amino acids, some of the amino acids are
coded for by more than one codon. The Genetic Code is
nothing more, really, than a list of the 64 possible
codons and the amino acids they correspond to.
Here's
a portion of the Genetic Code:
| Codon |
Amino Acid |
| AUG |
methionine |
| CUU |
leucine |
| GCA |
alanine |
| UUG |
leucine |
| CAG |
glutamine |
| CGA |
argenine |
And so on, and so on, and so on.
So, to figure out the order of amino acids in a protein,
all you have to do is look at the sequence of codons
on mRNA. Suppose you had a piece of mRNA with the following
sequence:
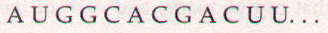
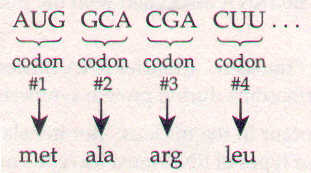
The codons are read in non-overlapping sequence,
like this:

So, for this piece of mRNA, the amino acid sequence
would be:
Now you can see how a nucleotide sequence on DNA can
specify a nucleotide sequence on RNA, and how that same
nucleotide sequence can specify an amino acid sequence
in a protein.
There are two final things to point out: first, the
codon AUG (methionine) is known as the "start" codon,
because it's the first codon on all mRNAs and methionine
is the first amino acid in all proteins. Second, three
of the 64 possible codons do not specify an amino acid.
They specify "stop." In other words, "stop translating,
the protein is finished." The three stop codons are UAA, UGA, and UAG.
|

